
WELCOME TO AQUAMEN

The Aquatic Environmental Management Association (AQUAMEN) was born in 2016 from the vision of four young engineering students specializing in the fisheries field, wishing to improve the management of aquatic resources on the Cameroonian coast. After graduating, these professionals spent eight years strengthening their skills in scientific research, management and governance of aquatic resources. Once the skills had been acquired, the legalization of AQUAMEN made it possible to bring together this dynamic team, with in-depth expertise in oceanography, limnology and hydrology, as well as in the conservation of aquatic biodiversity. Thanks to their specialized knowledge, AQUAMEN is committed to increasing the awareness of local communities on the state of resources and to developing concrete actions to improve the management of aquatic biodiversity and optimize the existing governance model.
Ecological assessmen

Implement in-depth studies to assess, identify and map coastal marine habitats essential to biodiversity while promoting the traditional knowledge of coastal communities. This axis is the abbreviated AQUA-RESEARCH program
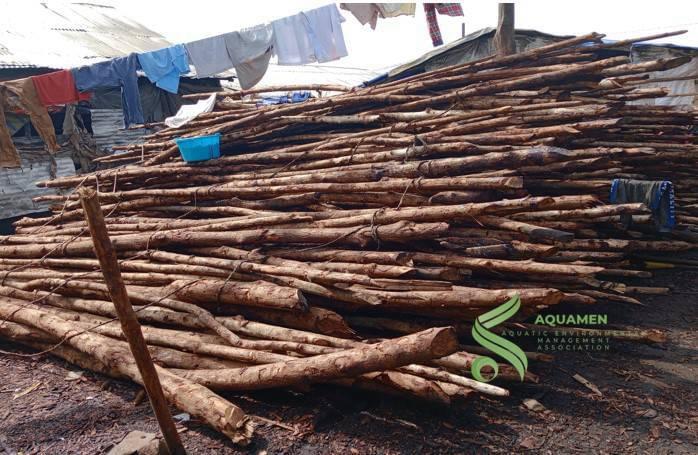


Integrated management of mangrove in cameroon with stakeholders and effective involvement of the local riparian community
Voir plus
Description :Mangroves, coastal ecosystems located at the interface
between land and sea, represent rich biotopes that play a fundamental
role in protecting biodiversity, regulating local climates, and preserving
coastal resources. However, these fragile environments face increasing threats,
including human-induced destruction, pollution, and climate change. The Cameroonian
coastline is no exception to this reality, as fishermen often cut down mangrove wood
for fish smoking and house construction. In this context, integrated mangrove management
emerges as an essential approach to ensure the sustainable use of these ecosystems while
preserving their vital ecological functions. Consequently, AQUAMEN has committed to
applying integrated management to Cameroon's mangroves, an approach that hinges on
simultaneously considering environmental, economic, and social dimensions. By
integrating these diverse aspects, decision-makers can formulate strategies that
promote sustainable development while addressing the needs of local communities
dependent on these ecosystems for their livelihoods. For example, activities such
as fishing, agriculture, and tourism are closely linked to mangroves but require
regulation to prevent compromising their health. AQUAMEN aims to tackle the
significant challenge of coordinating efforts among the various stakeholders
involved. Governments, NGOs, scientists, and local communities must collaborate to
establish effective conservation and management policies. This is why we are engaged
in awareness and education efforts directed at both local populations and
decision-makers, fostering a deeper understanding of the issues related to mangrove
degradation and its implications for daily life and the economy. We also plan to
undertake the restoration of degraded mangroves, which is a key component of
integrated management, but such efforts must be grounded in rigorous scientific
studies that consider biodiversity and local dynamics. Additionally, monitoring
mangroves through modern technologies, such as drones and satellite imagery, will
provide an effective means of tracking the state of these ecosystems and
evaluating the impact of implemented measures. Furthermore, it is crucial to
incorporate climate change considerations into mangrove management. These
ecosystems are not only vulnerable to the effects of climatic variations, but
they also play an essential role in mitigating such effects by serving as carbon
sinks. Investing in the resilience of mangroves against climatic hazards could,
in the long run, offer solutions for both biodiversity conservation and the
protection of coastal populations against extreme events. Ultimately, it is
imperative that management policies remain flexible and adaptive, taking into
account new scientific data and social changes. The active involvement of local
communities in the decision-making process is not only ethical but also
pragmatic, as their traditional knowledge and experience are invaluable assets
for effective and sustainable mangrove management.
Voir plus
Description :Mangroves, coastal ecosystems located at the interface between land and sea, represent rich biotopes that play a fundamental role in protecting biodiversity, regulating local climates, and preserving coastal resources. However, these fragile environments face increasing threats, including human-induced destruction, pollution, and climate change. The Cameroonian coastline is no exception to this reality, as fishermen often cut down mangrove wood for fish smoking and house construction. In this context, integrated mangrove management emerges as an essential approach to ensure the sustainable use of these ecosystems while preserving their vital ecological functions. Consequently, AQUAMEN has committed to applying integrated management to Cameroon's mangroves, an approach that hinges on simultaneously considering environmental, economic, and social dimensions. By integrating these diverse aspects, decision-makers can formulate strategies that promote sustainable development while addressing the needs of local communities dependent on these ecosystems for their livelihoods. For example, activities such as fishing, agriculture, and tourism are closely linked to mangroves but require regulation to prevent compromising their health. AQUAMEN aims to tackle the significant challenge of coordinating efforts among the various stakeholders involved. Governments, NGOs, scientists, and local communities must collaborate to establish effective conservation and management policies. This is why we are engaged in awareness and education efforts directed at both local populations and decision-makers, fostering a deeper understanding of the issues related to mangrove degradation and its implications for daily life and the economy. We also plan to undertake the restoration of degraded mangroves, which is a key component of integrated management, but such efforts must be grounded in rigorous scientific studies that consider biodiversity and local dynamics. Additionally, monitoring mangroves through modern technologies, such as drones and satellite imagery, will provide an effective means of tracking the state of these ecosystems and evaluating the impact of implemented measures. Furthermore, it is crucial to incorporate climate change considerations into mangrove management. These ecosystems are not only vulnerable to the effects of climatic variations, but they also play an essential role in mitigating such effects by serving as carbon sinks. Investing in the resilience of mangroves against climatic hazards could, in the long run, offer solutions for both biodiversity conservation and the protection of coastal populations against extreme events. Ultimately, it is imperative that management policies remain flexible and adaptive, taking into account new scientific data and social changes. The active involvement of local communities in the decision-making process is not only ethical but also pragmatic, as their traditional knowledge and experience are invaluable assets for effective and sustainable mangrove management.
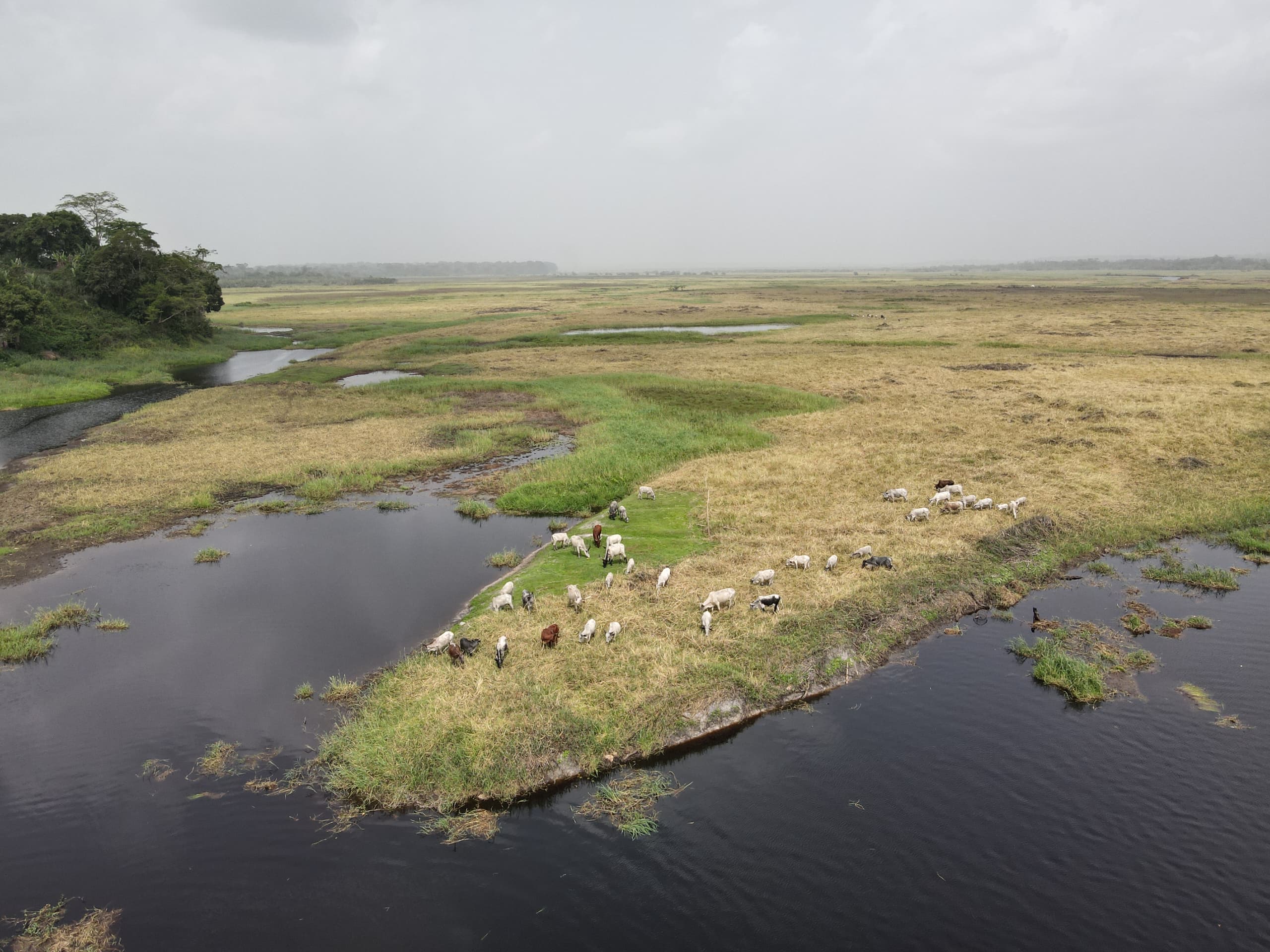

Conserving biodiversity and sustainably managing essential resources in the Nyong River region
Voir plus
The Nyong River, meandering through the South Region of Cameroon, represents a vital ecosystem
for both local fauna and flora. This waterway serves not only as a fundamental source of
livelihood for the surrounding communities but also harbors a rich biodiversity, including
several endemic and endangered species. However, it faces mounting threats such as the
proliferation of invasive plant species, climate change, and poaching of vulnerable species
like the African manatee. These challenges, exacerbated by climate variations, necessitate
immediate action to mitigate impacts and preserve the ecological wealth of the river.
Strengthening biodiversity conservation within the Nyong River ecosystem has thus become
an imperative priority. To achieve this, AQUAMEN will implement integrated and
participatory strategies. A key component of these strategies will be raising awareness
among local communities regarding the significance of biodiversity and the benefits of
sustainable resource management. Environmental education programs will be developed to
actively engage residents in the protection of ecosystems, while providing them with
sustainable alternatives to traditional practices such as fishing. Additionally,
promoting ecotourism could serve as a significant source of income for these communities
while fostering the conservation of natural habitats. The establishment of RAMSAR sites
along the Nyong River is also a crucial measure for protecting biodiversity. These areas
can act as refuges for endangered species and natural laboratories for scientific
research. Management of these sites will be conducted in collaboration with local
stakeholders to ensure that the needs and cultural values of the populations are
respected. Concurrently, monitoring the quality of water and aquatic ecosystems
will be enhanced through partnerships involving researchers and scientists alongside
local authorities
.
Voir plus
The Nyong River, meandering through the South Region of Cameroon, represents a vital ecosystem for both local fauna and flora. This waterway serves not only as a fundamental source of livelihood for the surrounding communities but also harbors a rich biodiversity, including several endemic and endangered species. However, it faces mounting threats such as the proliferation of invasive plant species, climate change, and poaching of vulnerable species like the African manatee. These challenges, exacerbated by climate variations, necessitate immediate action to mitigate impacts and preserve the ecological wealth of the river. Strengthening biodiversity conservation within the Nyong River ecosystem has thus become an imperative priority. To achieve this, AQUAMEN will implement integrated and participatory strategies. A key component of these strategies will be raising awareness among local communities regarding the significance of biodiversity and the benefits of sustainable resource management. Environmental education programs will be developed to actively engage residents in the protection of ecosystems, while providing them with sustainable alternatives to traditional practices such as fishing. Additionally, promoting ecotourism could serve as a significant source of income for these communities while fostering the conservation of natural habitats. The establishment of RAMSAR sites along the Nyong River is also a crucial measure for protecting biodiversity. These areas can act as refuges for endangered species and natural laboratories for scientific research. Management of these sites will be conducted in collaboration with local stakeholders to ensure that the needs and cultural values of the populations are respected. Concurrently, monitoring the quality of water and aquatic ecosystems will be enhanced through partnerships involving researchers and scientists alongside local authorities
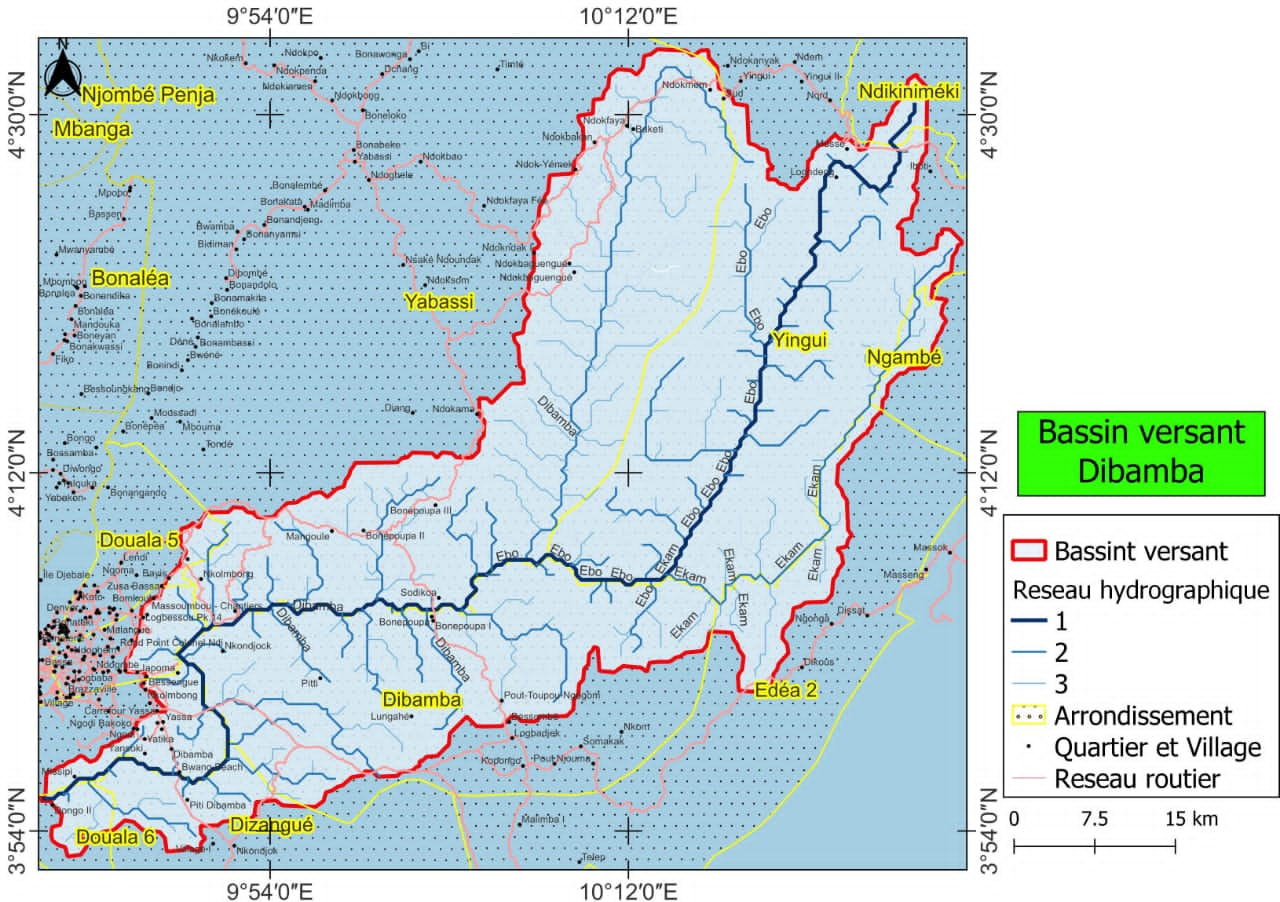
improving the understanding of the hydrology of the watersheds along the Cameroonian coast
Voir plus
Hydrology, as a scientific discipline, plays a pivotal role in the management of water
resources, particularly in coastal regions where hydrological systems are often subjected
to significant anthropogenic and environmental pressures. The coastal watersheds of Cameroon,
notably those of the Sanaga, Wouri, and Nyong rivers, are characterized by a diversity of
hydrological regimes influenced by various climatic and geographical factors. However, the
existing data on these systems remain incomplete and frequently unreliable. Enhancing our
hydrological understanding of these watersheds is essential for optimizing water resource
management and mitigating risks associated with flooding, coastal erosion, and pollution.
In response to this pressing situation, AQUAMEN has made the strategic decision to address
the growing challenges related to integrated water resource management by developing a
denser and more systematic hydrological data collection network. This initiative will
involve the installation of hydrometric and rain-gauge stations, alongside the
implementation of remote sensing systems that facilitate continuous, real-time
observation of hydrological parameters. Furthermore, hydrological modeling will
serve as a valuable tool for simulating watershed behavior in response to various
climatic and anthropogenic conditions. The application of region-specific numerical
models for the coastal area of Cameroon will allow for anticipatory assessments of
the impacts of climate variability and land use changes on the water cycle.
By integrating this modeling approach with collected field data, it will be possible
to develop prospective scenarios that will inform planning interventions and the
establishment of sustainable water resource management policies. AQUAMEN is also
committed to adopting a participatory approach that engages local communities,
decision-makers, and scientists. By raising awareness among populations about
hydrological issues, we promote a collaborative development of solutions tailored
to local realities. Initiatives focused on training and education regarding water
management practices, combining traditional knowledge with scientific innovations,
will further bolster community resilience in the face of hydrological challenges.
This comprehensive strategy underscores AQUAMEN's dedication to fostering a
sustainable and inclusive framework for water resource management in the coastal
regions of Cameroon
Voir plus
Hydrology, as a scientific discipline, plays a pivotal role in the management of water resources, particularly in coastal regions where hydrological systems are often subjected to significant anthropogenic and environmental pressures. The coastal watersheds of Cameroon, notably those of the Sanaga, Wouri, and Nyong rivers, are characterized by a diversity of hydrological regimes influenced by various climatic and geographical factors. However, the existing data on these systems remain incomplete and frequently unreliable. Enhancing our hydrological understanding of these watersheds is essential for optimizing water resource management and mitigating risks associated with flooding, coastal erosion, and pollution. In response to this pressing situation, AQUAMEN has made the strategic decision to address the growing challenges related to integrated water resource management by developing a denser and more systematic hydrological data collection network. This initiative will involve the installation of hydrometric and rain-gauge stations, alongside the implementation of remote sensing systems that facilitate continuous, real-time observation of hydrological parameters. Furthermore, hydrological modeling will serve as a valuable tool for simulating watershed behavior in response to various climatic and anthropogenic conditions. The application of region-specific numerical models for the coastal area of Cameroon will allow for anticipatory assessments of the impacts of climate variability and land use changes on the water cycle. By integrating this modeling approach with collected field data, it will be possible to develop prospective scenarios that will inform planning interventions and the establishment of sustainable water resource management policies. AQUAMEN is also committed to adopting a participatory approach that engages local communities, decision-makers, and scientists. By raising awareness among populations about hydrological issues, we promote a collaborative development of solutions tailored to local realities. Initiatives focused on training and education regarding water management practices, combining traditional knowledge with scientific innovations, will further bolster community resilience in the face of hydrological challenges. This comprehensive strategy underscores AQUAMEN's dedication to fostering a sustainable and inclusive framework for water resource management in the coastal regions of Cameroon
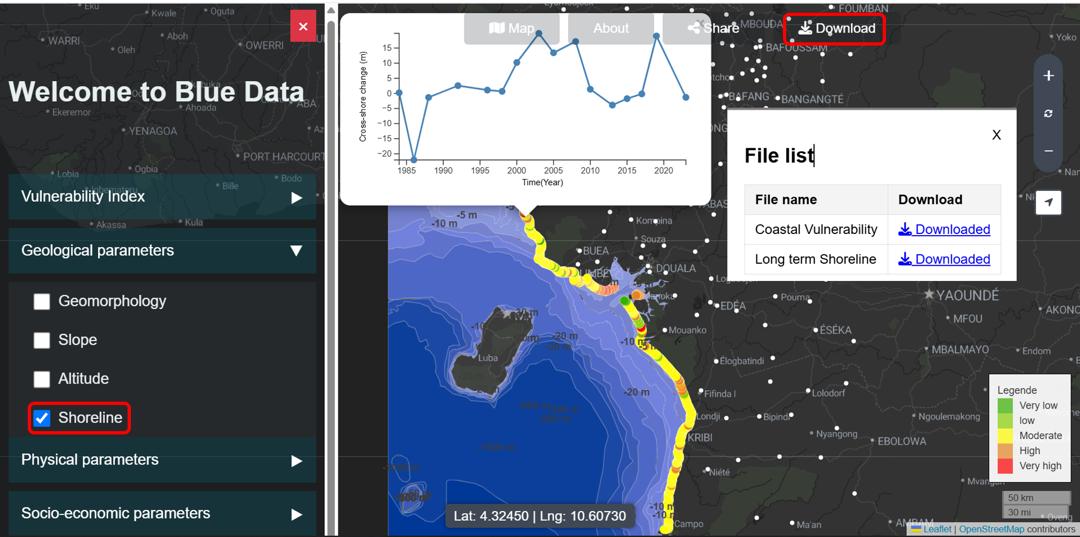
Blue Data : L'observatoire collaboratif pour la résilience du Golfe de Guinée
Voir plus
Face à la persistance de la pêche illégale et non déclarée (INN) sur les espaces marins et
côtiers non autorisés de la côte camerounaise, conjuguée à une érosion côtière progressive
et visible sur l’ensemble du littoral, la nécessité d’une réponse innovante et scientifique
solide devient cruciale pour renforcer sa gestion. En réponse à ce défi croissant, un système
de surveillance participatif a été développé (Blue Data) pour collecter en temps réel les
données locales et contextuelles, qui, combinées aux données satellitaires, seront analyser
en continu de manière automatique et précise, fournissant ainsi aux décideurs un outils
scientifique performant pour orienter les choix politique de gestion, renforcer la
gouvernance et anticiper sur les risques de l’espace côtiers.
Voir plus
Face à la persistance de la pêche illégale et non déclarée (INN) sur les espaces marins et côtiers non autorisés de la côte camerounaise, conjuguée à une érosion côtière progressive et visible sur l’ensemble du littoral, la nécessité d’une réponse innovante et scientifique solide devient cruciale pour renforcer sa gestion. En réponse à ce défi croissant, un système de surveillance participatif a été développé (Blue Data) pour collecter en temps réel les données locales et contextuelles, qui, combinées aux données satellitaires, seront analyser en continu de manière automatique et précise, fournissant ainsi aux décideurs un outils scientifique performant pour orienter les choix politique de gestion, renforcer la gouvernance et anticiper sur les risques de l’espace côtiers.
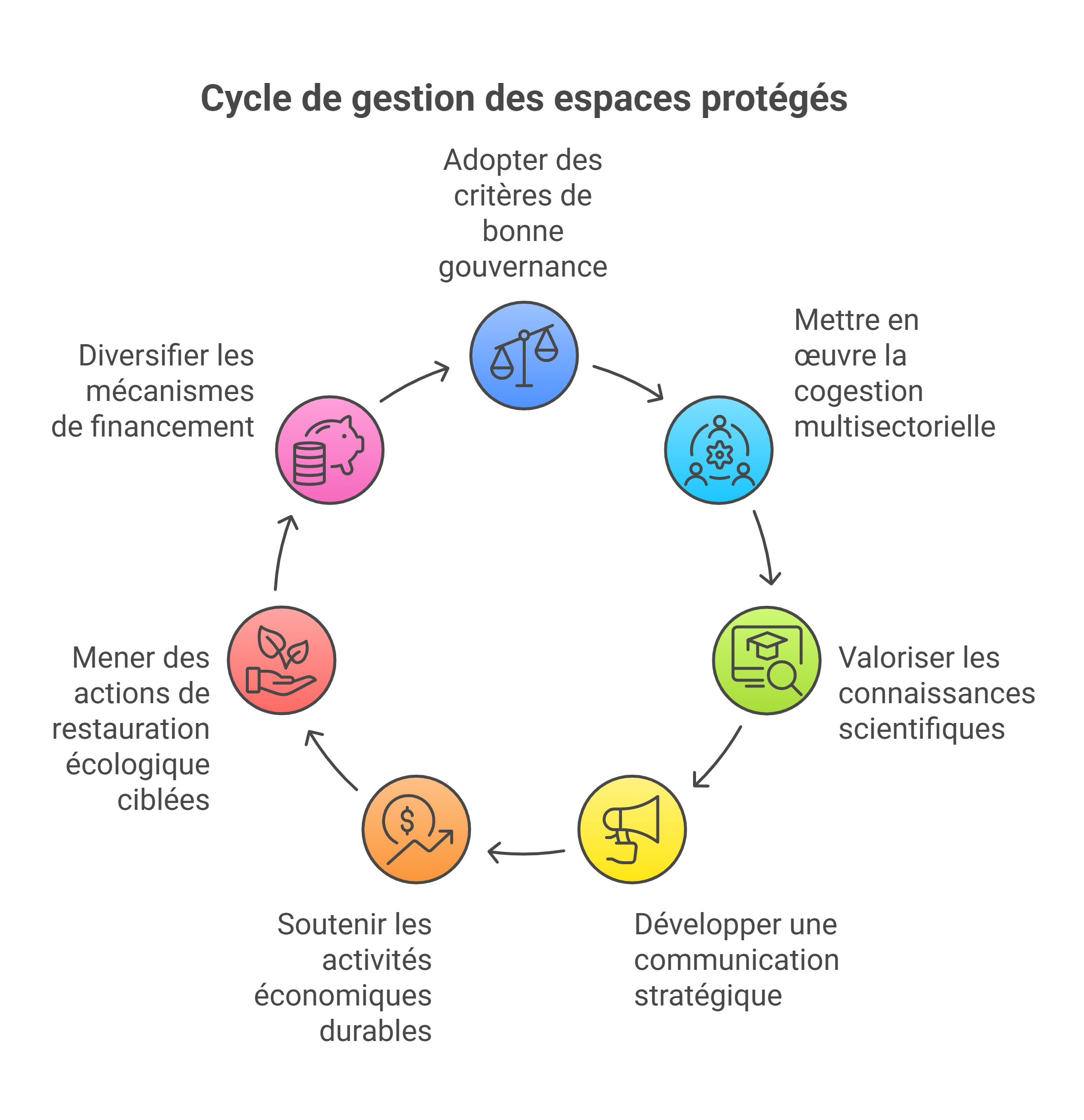
GECOP : Approche de gestion des espaces marin et côtier
Voir plus
Au Cameroun, les Aires Marines Protégées (AMP) et les Autres Mesures de Conservation
Efficace par Zone (AMCEZ) occupent une place stratégique dans la préservation de la
richesse biologique côtière. Cependant leur potentiel reste sous-exploité en raison des
défis majeurs liés à la gouvernance et la gestion adaptée. Face aux exigences du Cadre
mondial pour la biodiversité de Kunming-Montréal (COP15), qui met l’accent sur une
gouvernance équitable et une gestion efficace des zones protégées, AQUAMEN a mis en
place une approche baptisée GECOP (Gouvernance, Exploitation, Cogestion et Planification)
inspiré de plusieurs autres approches de gestion. Cette méthode innovante propose un cadre
intégré, participatif et flexible pour renforcer la gestion des espaces protégés marin et
côtier au Cameroun
Voir plus
Au Cameroun, les Aires Marines Protégées (AMP) et les Autres Mesures de Conservation Efficace par Zone (AMCEZ) occupent une place stratégique dans la préservation de la richesse biologique côtière. Cependant leur potentiel reste sous-exploité en raison des défis majeurs liés à la gouvernance et la gestion adaptée. Face aux exigences du Cadre mondial pour la biodiversité de Kunming-Montréal (COP15), qui met l’accent sur une gouvernance équitable et une gestion efficace des zones protégées, AQUAMEN a mis en place une approche baptisée GECOP (Gouvernance, Exploitation, Cogestion et Planification) inspiré de plusieurs autres approches de gestion. Cette méthode innovante propose un cadre intégré, participatif et flexible pour renforcer la gestion des espaces protégés marin et côtier au Cameroun
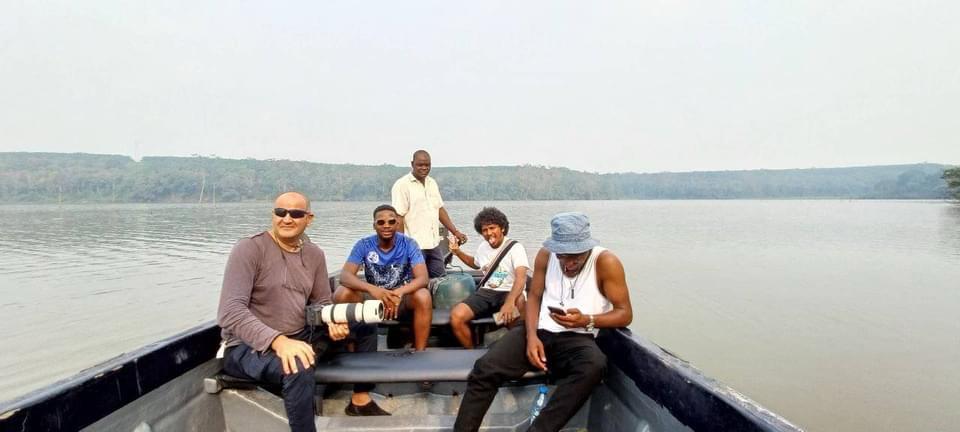

Ecological assessment
Voir plus
Implement in-depth studies to assess, identify and map coastal marine habitats essential
to biodiversity while promoting the traditional knowledge of coastal communities.
This axis is the abbreviated AQUA-RESEARCH program
Voir plus
Implement in-depth studies to assess, identify and map coastal marine habitats essential to biodiversity while promoting the traditional knowledge of coastal communities. This axis is the abbreviated AQUA-RESEARCH program

Community Awareness
Voir plus
Develop educational programs to raise awareness among local communities and the general public
of the importance of marine conservation and good resource management practices. This axis is
the abbreviated AQUA-COM program
Voir plus
Develop educational programs to raise awareness among local communities and the general public of the importance of marine conservation and good resource management practices. This axis is the abbreviated AQUA-COM program
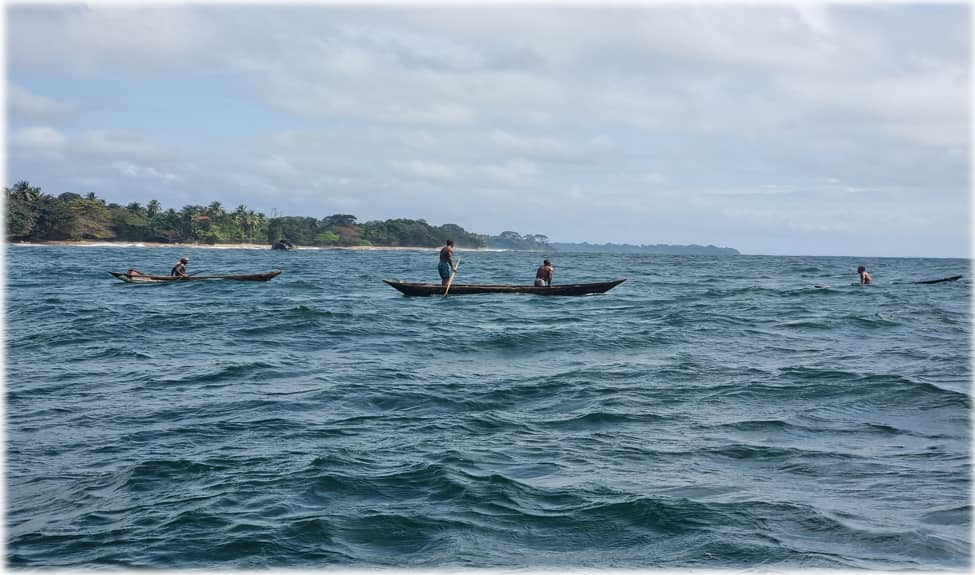

Develop sustainable livelihoods for the local riverside community
Voir plus
Implement an integrated approach that favors training in responsible fishing practices,
eco-tourism and the development of natural resources in order to contribute to harmonious
and environmentally friendly development. This axis is the abbreviated AQUA-INVEST program
Voir plus
Implement an integrated approach that favors training in responsible fishing practices, eco-tourism and the development of natural resources in order to contribute to harmonious and environmentally friendly development. This axis is the abbreviated AQUA-INVEST program
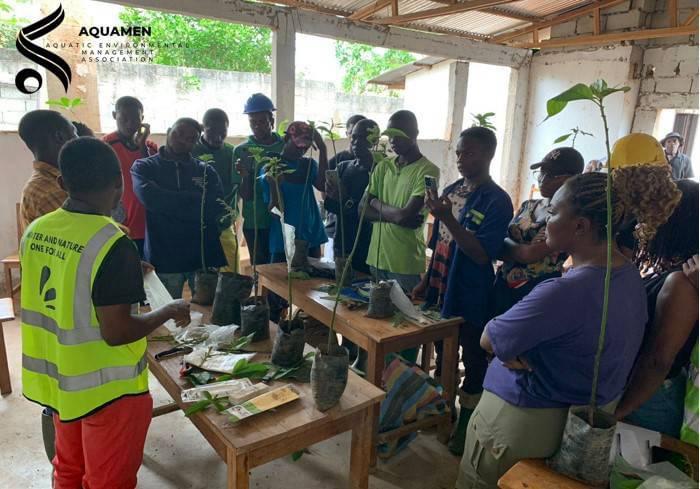

Strengthening the management and governance of aquatic biodiversity
Voir plus
Adopting an integrated approach combining the collaboration of stakeholders, the establishment
of monitoring and evaluation mechanisms will make it possible to identify threats to aquatic
ecosystems and adjust conservation strategies accordingly. This axis is the abbreviated
AQUA-GO program
Voir plus
Adopting an integrated approach combining the collaboration of stakeholders, the establishment of monitoring and evaluation mechanisms will make it possible to identify threats to aquatic ecosystems and adjust conservation strategies accordingly. This axis is the abbreviated AQUA-GO program

